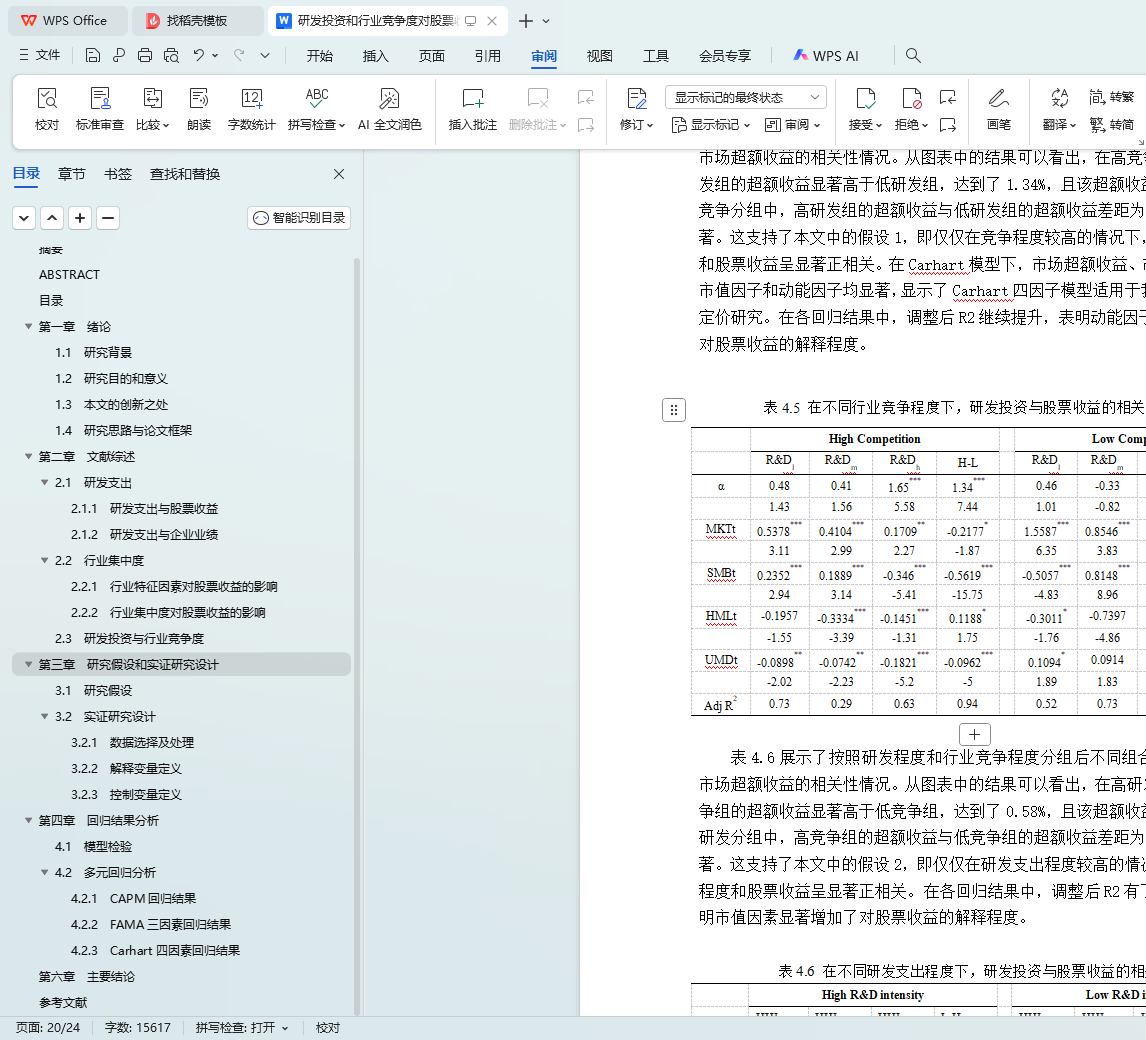
研发投资和行业竞争度对股票收益的影响:基于A股市场的实证研究 硕士论文
摘要
本文通过研究市场集中度和研发投资对股票收益的交互作用,解决了两个资产定价问题。这为股票收益与研发投资、股票投资与行业集中度的相关领域提供了新的视角。
在竞争性行业中,企业所从事的研发活动具有更大的风险。主要原因是在竞争行业中,企业面临的竞争对手较多,因此竞争对手在研发活动中取胜的概率更大;一旦竞争对手的研发得以完成,企业在本轮研发竞争中将以失败告终,其未来现金流将变为零。因此,行业的竞争程度提升了企业研发所需未来的现金流,而这使得企业在从事研发活动中需要更高的风险溢价得以补偿。而在高研发活动行业中,研发支出的提升同样增加企业在竞争过程中面临的风险;因此,在高研发支出时,高竞争性企业需要更高的风险溢价得以补偿。
这一理论基础在文中的实证分析中得以证实,即股票收益与研发支出的正相关性仅存在于竞争性行业中。与此同时,股票收益与行业竞争度的正相关性近存在于高研发支出股票中。
关键词:研发投资,行业竞争度,股票收益
The Impact of R&D Investment and Industry Concentration on Stock Returns: Empirical Study Based on China’s A-Share Market
Yibin Zhang
Directed by Wei Cen
ABSTRACT
This paper tackles two asset pricing puzzles by testing the joint effect of product market competition and R&D investment on stock returns, and it provides new perspectives on the positive competition-return and R&D-return relations that have drawn a fair amount of attention from economists.
In competitive industries, firms frequently must enter innovation races with many rivals for new products or technologies. The potential future cash flows associated with R&D projects are more likely to be extinguished in competitive industries because rivals could win the innovation race. Therefore, competition raises the exercise thresholds for R&D investment options and magnifies R&D-intensive firm's exposure to the systematic risk.
These insights are confirmed by the empirical findings that the positive R&D-return relation exists only in competitive industries and that the competition-return relation exists only among R&D-intensive firms.
In close, this study suggests that competition has a significant impact on R&D-intensive firms' risk and return profiles and thus independently drives a significant portion of the R&D premium. Moreover, this paper proposes a potential mechanism through which market structure affects a firm's risk dynamics, thereby providing a risk-based explanation for the heretofore puzzling competition-return relation.
KEY WORDS: R&D Investment, Industry Concentration, Stock Returns
目录