IPv4分组收发实验以及IPv4分组转发实验
IPv4分组收发实验以及IPv4分组转发实验
实验目的:
IPv4分组收发实验目的: 本实验通过设计实现主机协议栈中的IPv4协议,让我们深入了解网络层协议的基本原理,学习IPv4协议基本的分组接收和发送流程。另外,通过本实验,我们可以初步接触互联网协议栈的结构和计算机网络实验系统,为后面进行更为深入复杂的实验奠定良好的基础。
IPv4分组转发实验目的: 通过模拟实现路由器中的ipv4实验,从而使得我们对网络的观察视角由主机转移到路由器中,了解路由器是如何为分组转发路由的,通过了解路由转发表的功能和数据结构,能够初步设计简单的路由转发表。
实验内容:
IPv4分组收发实验: 根据计算机网络实验系统所提供的上下层接口函数和协议中分组收发的主要流程,独立设计实现一个简单的IPv4分组收发模块。
要求实现的主要功能包括:
(1)实现IPv4分组的基本接收处理功能,对于接收到的IPv4分组,检查目的地址是否为本地地址,并检查IPv4分组头部中其它字段的合法性。提交正确的分组给上层协议继续处理,丢弃错误的分组并说明错误类型。
(2)实现IPv4分组的封装发送根据上层协议所提供的参数,封装IPv4分组,调用系统提供的发送接口函数将分组发送出去。
IPv4分组转发实验;
(1)设计路由表数据结构。设计路由表所采用的数据结构。要求能够根据目的IPv4地址来确定分组处理行为(转发情况下需获得下一跳的IPv4地址)。路由表的数据结构和查找算法会极大的影响路由器的转发性能,有兴趣的同学可以深入思考和探索。
(2) IPv4分组的接收和发送。对前面实验(IP实验)中所完成的代码进行修改,在路由器协议栈的IPv4模块中能够正确完成分组的接收和发送处理。具体要求不做改变,参见“IP实验”。
(3) IPv4分组的转发。对于需要转发的分组进行处理,获得下一跳的IP地址,然后调用发送接口函数做进一步处理。
实验过程:
一、IPv4分组收发实验
因为实验使用的软件对新windows10兼容不佳,所以我使用virtual box 安装了window7 虚拟机,在虚拟机上安装好了实验使用的软件。
软件运行的截图:
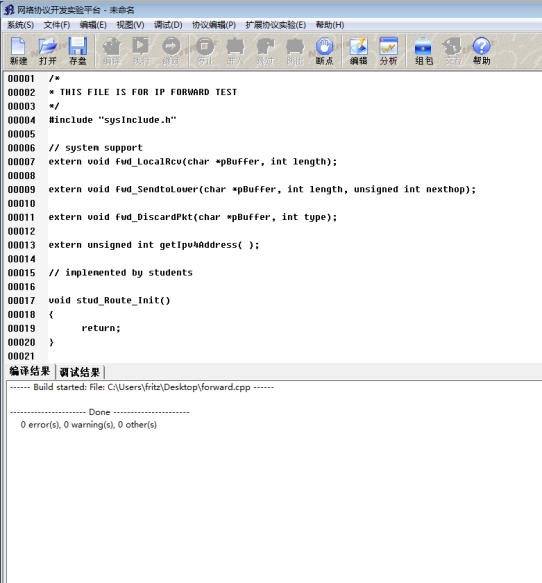
之后登录账号,选择好实验的类型,新建了一个实验的模板,实验的准备工作完成。
之后,首先开始实现ipv4的发送功能,为了便于为*pBuffer赋值,首先定义了一个结构体,作为ipv4的头部的数据结构。
结构体定义如下:
typedef struct ip_header
{
char version_header_len; // version + header length
char ToS; // Tos
unsigned short total_length; // total length
unsigned short identification; // identification
unsigned short flag_offset; // flag and offset
char ttl; // ttl
char protocol; // protocol type
unsigned short checksum; // check sum
unsigned int srcAddr; // source address
unsigned int dstAddr; // destiny address
} ip_header_type;
之后在stud_ip_Upsend函数中开始实现发送ipv4报文的功能。
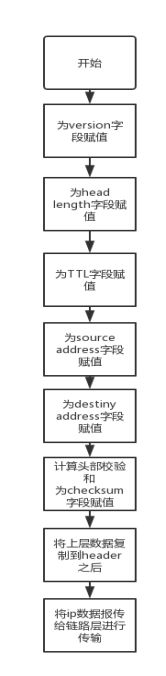
即为ip_header的每一个字段赋值,version的值固定为4,header length的值最少为5,表明ip 的header的长度最少为20字节,服务类型可以不指定,设为0,ip 数据报的总长度字段设置成 头部长度 + 数据长度,ip的标识字段设置成一个随机数,flag_offset由于本实验不需要考虑ip分组问题,全部设成0. TTL设置成函数传输的参数,protlcol(ip数据报传输的协议类型)也设置成函数传入的参数,checksum在初始化时先设成0, srcAddr 源ip地址设成函数传入的参数,dstAddr设成目的ip地址。
之后开始根据当前头部的信息,计算checksum 校验和, 计算的方法是:
首先把头部除checksum的字段每 16bit做二进制加法,得到一个和sum,之后,将sum的高16bit的值加到低16bit上,而这一过程要一直持续,直到最后的和的高16bit为0,因为在加到低16bit时,仍然可能发生进位。将最后的结果按位取反,赋给ip数据报header中的checksum字段。最后将上层传入的数据拷贝到ip报头部之后。
ip数据报的就构造完成,调用ip_SendtoLower()函数将ip数据报交给下层协议去传输。
流程框图:
ip数据报的接收:
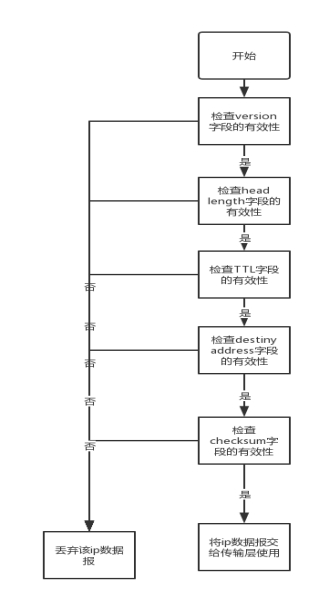
依次检查ip头部的每一个字段。先检查version是否为4,如果不是,就调用ip_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_IP_TEST_VERSION_ERROR); 并返回1,表示拒绝接收这个ip数据报,并返回错误的类型(version错误)。之后判断 header的长度字段, 如果小于5,则调用
ip_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_IP_TEST_HEADLEN_ERROR); 并返回1。
之后判断TTL的值,如果等于0,则调用ip_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_IP_TEST_TTL_ERROR); 并返回1.
之后判断目的地址是否是广播地址或者自己的ip地址(通过调用getIpv4Address()获得),如果不是,则调用ip_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_IP_TEST_DESTINATION_ERROR) ,表示目的地址错误。最后,使用发送ip数据报中的 计算checksum的算法,计算得到一个值,如果checksum正确的话,应该是等于0,如果不是,则调用ip_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_IP_TEST_CHECKSUM_ERROR); 来丢掉这个ip数据报。 最后,经过层层检查后没有错误的数据报将调用ip_SendtoUp()函数交给传输层使用。
ip数据报的接收部分完成。
这个函数的流程框图如下:
IPv4分组转发实验:
使用的数据结构说明: 在这个实验中,我使用了map的数据结构(通过key 与 value一一映射),通过目的地址可以快速的索引到下一条的ip地址。
同时沿用了上一个实验ipv4的发送和接收中的ip报文的header 结构体,帮助更好的解析收到的ip数据报。
在 stud_Route_Init()函数中初始化map数据结构,清空其中已有的数据。
在 stud_route_add(stud_route_msg *proute)函数中,将收到的stud_route_msg,计算出目的地址,创建一条新的<key,value>, 将目的地址作为key,将下一条的ip地址作为value,然后将这一个记录加入到 table(map数据结构)中。
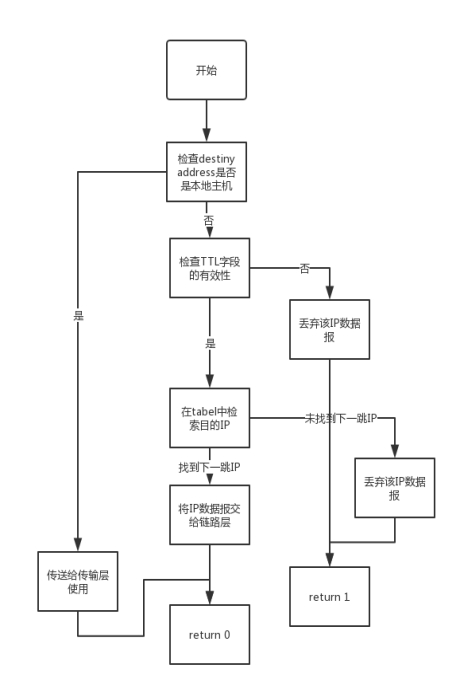
stud_fwd_deal(char *pBuffer, int length)函数中首先判断目的地址是否是本机的,如果是,就直接接收,如果不是,判断TTL的有效性(>0),如果无效,调用fwd_DiscardPkt()函数丢弃ip数据报。 之后将TTL的值-1,表示经过一次转发,然后通过dstAdr在table中进行索引,如果能够索引得到,则调用fwd_SendtoLower函数,将数据报传给下一条IP,如果未能检索到,就调用fwd_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_FORWARD_TEST_NOROUTE);函数丢弃该数据帧。
这个函数的程序框图:
在路由表的数据存储时,我选用了hash map的存储方式,这种数据结构的优势是在检索时,时间复杂度可以达到O(n),在性能方面有很大的优势。更多的优化我觉得还可以从IP的合并上努力,定期更新转发表,将其中可以合并的项和过期项进行合并和清理,来提高检索时的性能。
实验结果:
IPv4分组收发实验:
首先将编写好的代码保存到一个文件,然后点击编译按钮,得到如下的编译结果,没有编译的警告和错误。
运行结果如下:
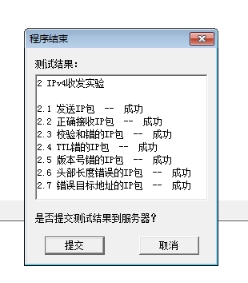
系统评价如下:
IPv4分组转发实验:
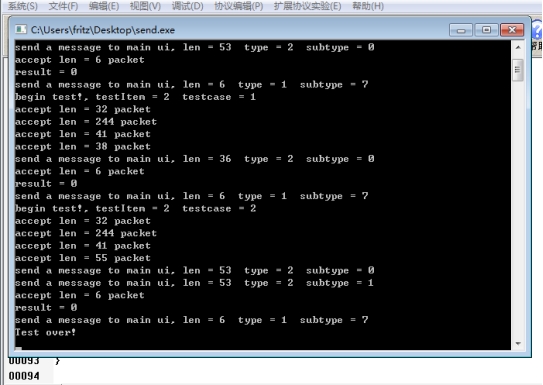
与上面实验同样的操作,编译代码,运行代码,运行截图如下:
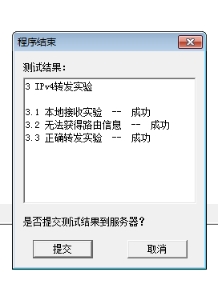
系统的评价结果如图:
问题讨论:
在实验时,遇到了网络字节序与机器字节序不同的问题,即在计算机系统课程中学过的大端序和小端序存储数据的两种方式。由于在机器中使用小端序存储数据有性能方面的优势,所有大部分的机器在存储数据时,采用小端序的存储方式,但是在人读数据时,习惯使用的是大端序,所以在网络传输等用途中使用的是大端序(网络序)。
所以在编写程序过程中需要将从网络获取的IP数据报中的short,int等类型的数据转成小端序读取和运算,同样,将程序中的数字写入到IP数据报中时,需要将小端序转换成大端序(网络字节序),不然最后程序运行的结果是错误的。
心得体会:
通过IPv4的收发实验和分组转发实验,使得我对ipv4的数据报格式有了深刻的记忆和理解,对于每个数据段的作用有了清晰的认识,同时对计算机网络中 网络层有了较深的理解,理解了ip数据分组如何在路由器之间进行转发,如何构造转发表的数据结构使得检索转发表的性能尽可能的高。通过这次的实验,为以后计算机网络的学习和应用打下了坚实的基础。
附录: 源代码
Send_receive.cpp
/*
* THIS FILE IS FOR IP TEST
*/
// system support
#include "sysInclude.h"
extern void ip_DiscardPkt(char *pBuffer, int type);
extern void ip_SendtoLower(char *pBuffer, int length);
extern void ip_SendtoUp(char *pBuffer, int length);
extern unsigned int getIpv4Address();
// implemented by students
typedef struct ip_header
{
char version_header_len; // version + header length
char ToS; // Tos
unsigned short total_length; // total length
unsigned short identification; // identification
unsigned short flag_offset; // flag and offset
char ttl; // ttl
char protocol; // protocol type
unsigned short checksum; // check sum
unsigned int srcAddr; // source address
unsigned int dstAddr; // destiny address
} ip_header_type;
int stud_ip_recv(char *pBuffer, unsigned short length)
{
void *ip;
ip = pBuffer;
if (((ip_header_type *)ip)->version_header_len >> 4 != 4)
{
ip_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_IP_TEST_VERSION_ERROR);
return 1;
}
else if ((((ip_header_type *)ip)->version_header_len & 0xf) < 5)
{
ip_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_IP_TEST_HEADLEN_ERROR);
return 1;
}
else if (((ip_header_type *)ip)->ttl == 0)
{
ip_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_IP_TEST_TTL_ERROR);
return 1;
}
else if (ntohl(((ip_header_type *)ip)->dstAddr) != getIpv4Address() && ntohl(((ip_header_type *)ip)->dstAddr) != 0xffffffff)
{
ip_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_IP_TEST_DESTINATION_ERROR);
return 1;
}
else
{
// caculate check sum
unsigned int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
sum += (unsigned int)(*((unsigned char *)ip + 2 * i) << 8);
sum += (unsigned int)(*((unsigned char *)ip + 2 * i + 1));
}
while ((sum & 0xffff0000) != 0)
{
sum = (sum & 0xffff) + ((sum >> 16) & 0xffff);
}
unsigned short short_check = ~sum;
if (short_check != 0)
{
ip_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_IP_TEST_CHECKSUM_ERROR);
return 1;
}
ip_SendtoUp((pBuffer + sizeof(ip_header_type)), length - sizeof(ip_header_type));
return 0;
}
}
int stud_ip_Upsend(char *pBuffer, unsigned short len, unsigned int srcAddr,
unsigned int dstAddr, byte protocol, byte ttl)
{
unsigned int seed = 5;
unsigned int r;
void *ip;
srand(seed);
r = rand();
ip = malloc(sizeof(ip_header_type) + len);
((ip_header_type *)ip)->version_header_len = (4 << 4) + 5;
((ip_header_type *)ip)->ToS = 0;
((ip_header_type *)ip)->total_length = htons(sizeof(ip_header_type) + len);
((ip_header_type *)ip)->identification = htons(r);
((ip_header_type *)ip)->flag_offset = htons(0);
((ip_header_type *)ip)->ttl = ttl;
((ip_header_type *)ip)->protocol = protocol;
((ip_header_type *)ip)->srcAddr = htonl(srcAddr);
((ip_header_type *)ip)->dstAddr = htonl(dstAddr);
// calculate check sum
unsigned int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (i != 5)
{
sum += (int)(*((unsigned char *)ip + 2 * i) << 8);
sum += (int)(*((unsigned char *)ip + 2 * i + 1));
}
}
while ((sum & 0xffff0000) != 0)
{
sum = (sum & 0xffff) + ((sum >> 16) & 0xffff);
}
((ip_header_type *)ip)->checksum = htons(~sum);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
*((char *)ip + sizeof(ip_header_type) + i) = *(pBuffer + i);
}
ip_SendtoLower((char *)ip, len + sizeof(ip_header_type));
return 0;
}
Farward.cpp
/*
* THIS FILE IS FOR IP FORWARD TEST
*/
#include "sysInclude.h"
#include <map>
// system support
extern void fwd_LocalRcv(char *pBuffer, int length);
extern void fwd_SendtoLower(char *pBuffer, int length, unsigned int nexthop);
extern void fwd_DiscardPkt(char *pBuffer, int type);
extern unsigned int getIpv4Address();
// implemented by students
typedef struct ip_header
{
char version_header_len; // version + header length
char ToS; // Tos
unsigned short total_length; // total length
unsigned short identification; // identification
unsigned short flag_offset; // flag and offset
char ttl; // ttl
char protocol; // protocol type
unsigned short checksum; // check sum
unsigned int srcAddr; // source address
unsigned int dstAddr; // destiny address
} ip_header_type;
map<unsigned int, unsigned int> table;
void stud_Route_Init()
{
table.clear();
return;
}
void stud_route_add(stud_route_msg *proute)
{
unsigned int destAdr = (ntohl(proute->dest)) & (0xffffffff << (32 - htonl(proute->masklen)));
unsigned int nextAdr = (ntohl(proute->nexthop));
table.insert(map<unsigned int, unsigned int>::value_type(destAdr, nextAdr));
return;
}
int stud_fwd_deal(char *pBuffer, int length)
{
void *ip;
ip = pBuffer;
unsigned int destAdr = ntohl(((ip_header_type *)pBuffer)->dstAddr);
if (destAdr == getIpv4Address())
{
fwd_LocalRcv(pBuffer, length);
return 0;
}
// ttl equal to 0 , means it can't be transported anymore
if (((ip_header_type *)ip)->ttl == 0)
{
fwd_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_IP_TEST_TTL_ERROR);
return 1;
}
map<unsigned int, unsigned int>::iterator iterator;
iterator = table.find(destAdr);
if (iterator != table.end())
{
((ip_header_type *)ip)->ttl -= 1;
// update the check sum
unsigned int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (i != 5)
{
sum += (int)(*((unsigned char *)ip + 2 * i) << 8);
sum += (int)(*((unsigned char *)ip + 2 * i + 1));
}
}
while ((sum & 0xffff0000) != 0)
{
sum = (sum & 0xffff) + ((sum >> 16) & 0xffff);
}
((ip_header_type *)ip)->checksum = htons(~sum);
fwd_SendtoLower(pBuffer, length, iterator->second);
return 0;
}
else
{ // can't find next ip from forward table
fwd_DiscardPkt(pBuffer, STUD_FORWARD_TEST_NOROUTE);
return 1;
}
}

