日处理240吨魔芋生产葡甘聚糖改性膜车间设计
 摘要
摘要
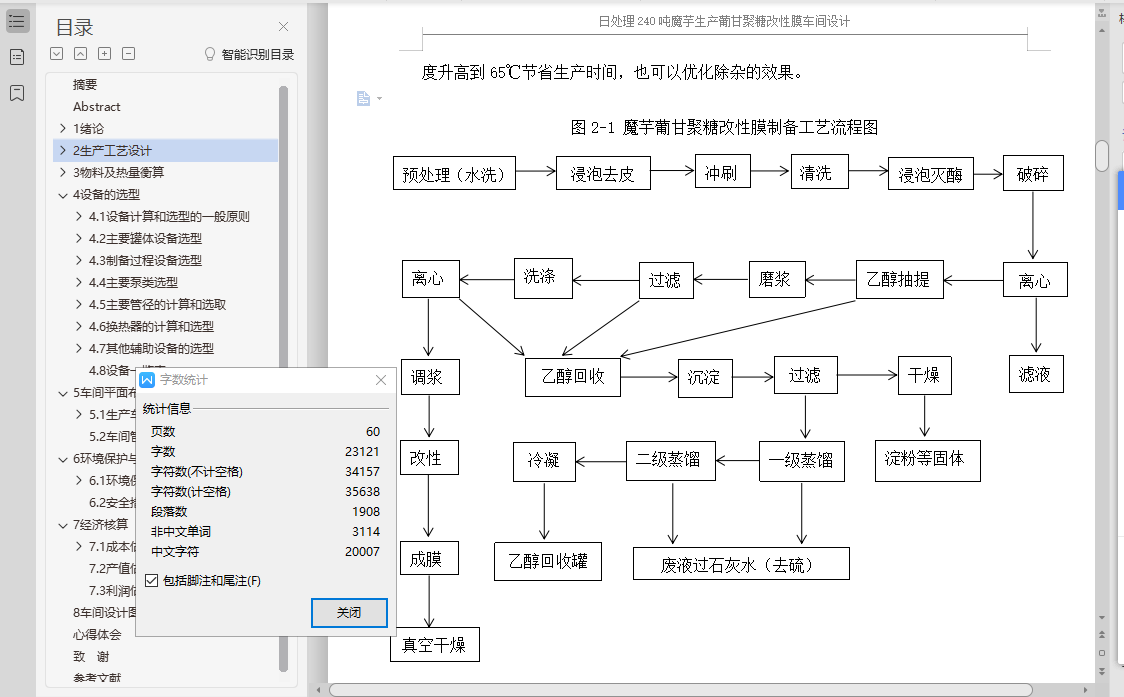
本设计采用有机湿法加工鲜魔芋以提取葡甘聚糖,利用碱液去皮,乙醇作为阻溶剂,通过浸泡灭酶,破碎,利用葡甘聚糖不溶于乙醇的特性,将破碎好的魔芋至于平转浸出器中用乙醇进行反复抽提,磨浆,过滤等工艺得到葡甘聚糖,将得到的葡甘聚糖和壳聚糖、聚乙烯醇溶液,按照质量比为2:2:1加水溶解混合均匀后进行共混改性,成膜后经过真空干燥得到此设计的最终产品。与传统干法相比,此设计可以有效克服硫含量残留过高、葡甘聚糖纯度不高等问题。
此设计是以鲜魔芋作为生产改性膜的原料,研究制定了其生产工艺流程,并据此进行相应的物料及热量衡算,根据实际成产的处理量和工艺需求进行设备、管道尺寸的设计和选型,以及车间平面的整体布置,最后对车间建造的成本和生产的经济效益进行了初步的预算和评估,并根据实际生产状况,绘制了说明书、工艺流程图、车间平面布置图与车间立剖图。
关键词:魔芋 葡甘聚糖 改性膜 湿法
Abstract
This design uses organic wet process to process fresh konjac to extract glucomannan, and use alkaline solution to peel, ethanol as a resistance solvent, soak to kill the enzyme, break down; And then use the insoluble properties of glucomannan in ethanol, glucomannan is obtained from the broken konjac by repeated extraction with ethanol in a flat rotary extractor, pulp grinding, filtration, etc. The resulting glucomannan and chitosan, polyvinyl alcohol solution were mixed and modified according to the mass ratio of 2:2:1 and water, and the final product was obtained after vacuum drying. Compared with traditional dry process, this design can effectively overcome the difficulties of high sulfur content and poor purity of glucomannan.
This design takes the fresh konjac as the raw material for the production of the modified membrane and determines its production process, and then carries out the related material balance calculation and heat balance calculation. According to the corresponding quantity, to design and select the size of the equipment and pipeline, arrange the production workshop; As well as the workshop design cost and the production economy has been conducted initial budget and evaluation; According to the actual production conditions, makes the specification,
drawn process flow chart, workshop layout and workshop profile.
Key words: konjac; wet method; glucomannan; modified membrane
目录

